Functional specification documents: the complete guide

Functional specification documents help you create a product users will love. Learn what they are and how to put one together!
Mitigating risk is one of the most valuable things you can do on a project. Reducing any potential costly problems or wasteful actions makes for a very smooth design and development process. It also puts a smile on stakeholders’ faces and boosts efficiency.
One way to ease the UX design headaches and create a better line of communication between your team is by creating and using a functional specification document, which acts as a single source of truth for the project ahead.
In this article, we’ll explore what a functional specification document is, why your team needs one and how to make one.
- Understanding functional specifications
- What is functional specification documentation?
- Why use functional specification documentation?
- Who is functional specification documentation for?
- Roles involved in functional specifications definition
- How to define functional specifications
- Functional specification document templates
- Visualize functional specifications and generate documents
Functional specifications are like the blueprint for any software project. They outline everything the system needs to do, ensuring everyone – from developers to designers to stakeholders – is on the same page about what’s being built.
But what sets functional specifications apart from technical ones?
Functional specifications focus on what the system should do, while technical specifications dive into how the system will actually work. Think of it like this: if functional specs are the detailed map guiding your journey, technical specs are the engineering behind the car you’re driving.
The right time to create a functional specification is during the early planning stages of a project. Before any code is written or designs are finalized, it’s important to have this document in place. It lays the foundation and fits seamlessly into the project’s overall lifecycle, acting as a guidepost through design, development, and even testing.
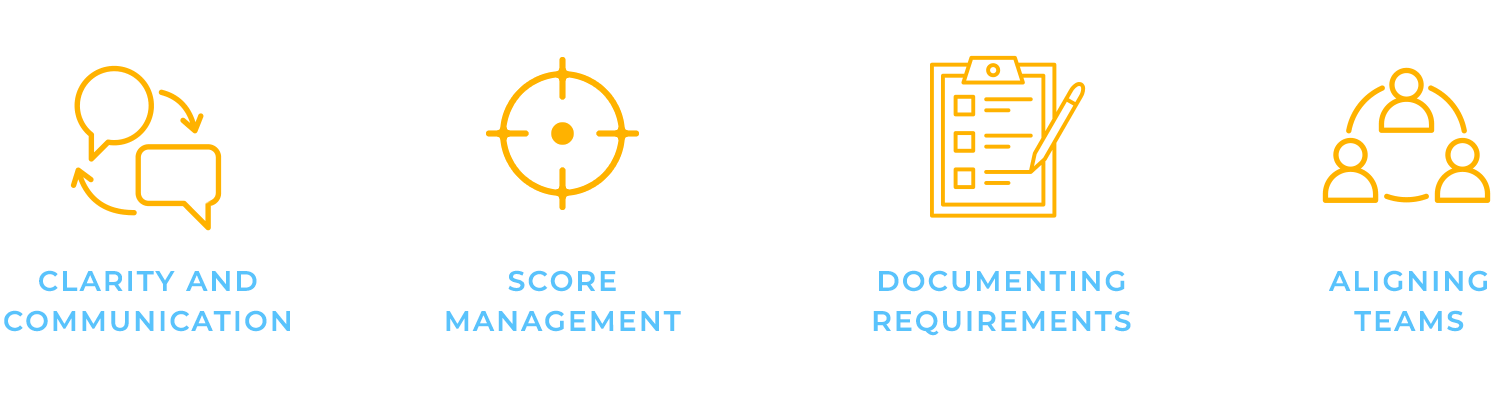
Functional specifications serve several important purposes:
1. Clarity and communication
At their core, these documents provide clear, detailed instructions for developers, designers, and stakeholders. This ensures that everyone understands what needs to be done and why it’s important.
2. Scope management
Functional specifications prevent scope creep by clearly laying out which features are included and which aren’t in the project. Without this clarity, teams can easily find themselves overwhelmed by unexpected features or changes.
3. Documenting requirements
They also capture all the user and business requirements. They make sure that the product being built solves the right problems and meets the expectations of everyone involved.
4. Aligning teams
A good functional specification aligns expectations across different teams – design, development, QA, and stakeholders. With this shared understanding, teams can work together more smoothly, avoiding costly misunderstandings down the road.
Now that we’ve covered why functional specifications are essential, let’s jump into the document itself. A functional specification document is more than just a list of tasks – it’s the foundation that holds everything together. It keeps everyone aligned, making sure that developers, designers, and stakeholders stay on the same page.
Let’s take a closer look at what a typical functional specification document includes.
Every great project starts with a clear purpose. The project overview gives a snapshot of what’s going on: what problem are we solving? What’s the main goal? It’s like the “why” behind everything. This part sets the stage and helps everyone understand where things are headed, without getting bogged down in the finer details yet.
Who’s involved, and who’s responsible for what? That’s what this section covers. But it’s more than just a list of names. It shows how everyone fits into the project puzzle, from the product manager to the designers, so that everyone knows who to turn to when questions come up. Think of it as the project’s team roster.
Understanding who will use the product is just as important as knowing how to build it. This section paints a picture of the users – their roles, their goals, and what they need from the product. By defining these personas, you ensure that the product is designed with real users in mind, not just abstract ideas.
Here’s where things get a little more practical. Use cases and scenarios bring the product to life by showing how users will interact with it. Whether it’s a simple action or a complex flow, this section lays out the typical situations a user might face and how the product will help them achieve their goals. It’s almost like telling the product’s story, with each use case acting as a different chapter.
This is where we dive into the core of the product. The functional requirements spell out exactly what the product needs to do, feature by feature. It’s the heart of the document, giving developers a clear direction on how to bring the product to life. But it’s not just a dry list – it’s about solving real problems and creating value for users and the business.
Every system has its own set of rules, and this section is all about making those clear. Business rules outline the logic and conditions that need to be followed, ensuring that everything works as it should. Whether it’s a specific workflow or a complex decision process, this part lays down the ground rules for how the system will behave.
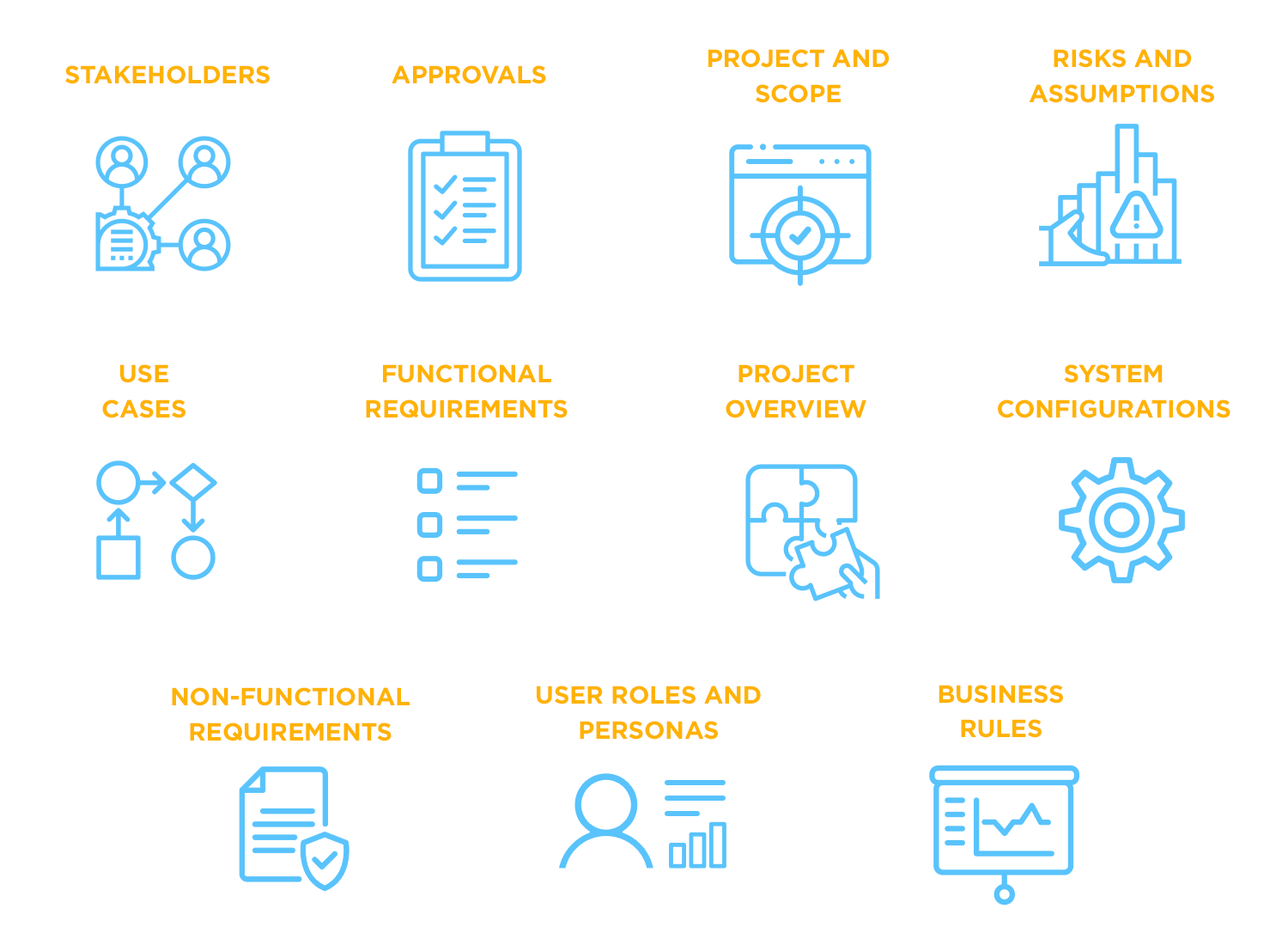
Getting sign-off from key players is essential before moving forward. This section keeps track of which features and decisions have been approved by stakeholders, ensuring everyone is on the same page. It’s the green light for the project to proceed without any surprises later on.
Scope is all about boundaries – what’s in and what’s out. This section makes sure everyone understands what the project will tackle and what it won’t. It helps manage expectations and avoids that sneaky feature creep that can derail timelines and budgets.
No project is without its risks. This part of the document highlights potential risks and assumptions, whether they’re technical challenges, budget constraints, or timeline concerns. If you flag these early, the team can plan ahead and avoid getting blindsided later.
Not everything is about features. Non-functional requirements focus on the product’s overall qualities, like performance, security, and usability. These are the things that make sure the product works well, feels intuitive, and meets user expectations beyond just delivering features.
Here’s where we get into the nuts and bolts of how the system will be set up. This section outlines the steps needed to configure the product, whether it’s creating user accounts or adjusting settings. It makes sure the system is ready to roll when the time comes.
Think about beginning writing a novel without planning. Is it possible? Maybe. Is it likely to succeed? You bet your life it isn’t. So imagine writing a piece of software into existence in code without planning! Your functional specification documentation serves as a roadmap for your developers.
Development is difficult and bug-prone enough as it is without having them write line after line of code on the edge of their seat with no structure or plan to guide them. In fact, most developers worth their salt won’t code without one to begin with.
Joel Spolsky certainly agrees that not having a functional specification document means spending way more time on coding and producing code that’s less efficient and of a lower quality and that will make it harder to fix bugs at a later time. You also risk ending up with an incohesive product that doesn’t serve its purpose.
Another reason to use functional specification documents before designing products or product features is to avoid running into the infamous design by committee conundrum. This is because functional specification documents are a way of getting everybody on board and dispelling personal assumptions about the product’s features so that you can create features that will solve real problems for your users.
Once the process of requirements gathering and the functional specification has been established, you’ll find that everything runs much more smoothly. Everyone will know what they’re doing and will be operating from the same source of truth, with less back-and forth-between different departments.
The fact everyone is involved and all the stakeholder’s roles are specified, along with what is expected of each department means there are no gray areas when it comes to getting tasks done. No stone is left unturned in the functional specifications document, meaning everyone can get on with their job and ensure that no detail is left out.
Lastly, having a functional specifications document from the start with all the features of the solution that you’re solving for the user well-defined will help prevent the dreaded feature creep.
Functional specification documents prevent unwanted design changes, sudden pivots or direction changes initiated by the client or other stakeholders. This is because, if you’ve done your functional specifications document right, it already provides a comprehensive answer to the question raised by the user’s problem and provides an adequate solution. Anything surplus to that is unnecessary.
Functional specification documents are primarily meant for developers, as they’re the ones who will code the solution for the user. However, these documents aren’t just for developers. They should be clear and accessible to everyone on the team, including designers, stakeholders, and the client. It’s crucial that this document acts as a shared resource – something everyone can refer back to throughout the project. In many ways, it’s the glue that keeps the entire team connected.
For developers, having a functional specification in hand before they start coding is incredibly valuable. It lays out the expectations and gives them a clear understanding of what the software should do. Without it, developers often run into problems later in the process, realizing that parts of the system don’t work as expected because there was no solid plan from the start. Using plain language and visuals like diagrams makes it even easier for everyone to grasp how the system will function.
Writing a functional specification document is rarely the job of one person. In most cases, a product manager leads the effort, but they don’t do it alone. They collaborate with UX designers, developers, clients, and other stakeholders to make sure everything is covered.The team gets everyone on the same page and backs the project’s direction by involving people from different departments early on.
Putting together a functional specification document isn’t something that happens in isolation – it’s a collaborative process involving a range of people with different expertise. Each plays a key part in getting things right. Here’s a look at who’s involved.
They are at the heart of gathering all the necessary details. Business analysts and product managers understand the goals of the project from both the business and user perspectives. They take big ideas and shape them into clear steps, ensuring the product meets its objectives. They’re the connectors, making sure the vision is clear for everyone involved.
After the goals are outlined, the designers step in. Their role is to create the UI design, layouts and interactions that people will engage with. Designers turn ideas into wireframes and mockups, working out how everything will look and function. They focus on how users will interact with the product, balancing simplicity with usability.
Developers are the builders. Once the plan is in place, they transform those designs into working software. But they don’t just follow instructions. Developers often provide essential input during planning, identifying what’s technically possible and suggesting improvements. This back-and-forth helps avoid unnecessary problems later and ensures the product functions smoothly.
Key users are the people who understand exactly what’s needed from the software. They know the ins and outs of daily tasks and the challenges that need solving. Their feedback is crucial to making sure the product addresses real needs and performs well in actual use.
Gather requirements by listening to the client and carrying out vigorous user research. At this stage, you’ll be writing down a lot of information. To manage all this information, you can use a requirements gathering tool. As you document these requirements, make sure that each one is specific, measurable, and unambiguous. This clarity is key to avoid confusion and reduce the need for future rework. Also, prioritize these requirements to align closely with the business objectives, ensuring they can be easily traced throughout the project lifecycle.
Identification of assumptions and constraints: Start your project right by outlining any potential assumptions and limitations that could impact the project’s reach, schedule, or how you use resources. Think about things like technical hurdles, rules you have to follow, how much money you have, or what the client wants specifically.
Strategies for managing and mitigating assumptions and constraints: Develop strategies to manage these assumptions and mitigate constraints. This might involve contingency planning, increasing budget allocations, or adjusting project timelines. Clearly documenting these strategies in the functional specifications can help prevent potential challenges and ensure smoother project execution.
After your prototype is complete, you can then initiate your first round of user testing to test out you and your client’s initial assumptions, i.e. everything about the user flow, the users’ mental models, and how they use the software. Most importantly, though, you can test that these features are actually usable for your main personae.
If the testing confirms your assumptions, then you start to write up your functional specification document. This document will serve as a blueprint for developers to code the final product.
Don’t attempt to create a functional specification document in isolation. Rather, if it’s possible, try to include at least one person from each department involved in the product’s development, including the client. By including different viewpoints, we make sure the document covers all the important angles. There are a few good reasons to get insights from different teams:
Better understanding: Each team brings something different to the table. They might know about technical limits, what customers want, or how the day-to-day work will be affected.
Fewer mistakes: When everyone checks the plan, it’s easier to catch problems early. This saves time and money later on.
Stronger teamwork: If people help write the plan, they’ll be more excited to work on the project. This makes the whole team work better.
This collaborative approach makes sure that the document reflects a comprehensive understanding of the project from all angles.
Firstly, it helps to use software that has good version control. Many functional specification documents are written in Microsoft Word, however, Google Docs tends to allow for better version control, something which is crucial in product development.
Often, developers complain about messy version control in Word documents and not being able to see specifically when and where a certain change was made. There’s also the case that it’s far easier to keep changes to a document synced in the cloud using a Google Doc.
For the most part, your functional specification document is going to be written in non-convoluted language. The reason for this is because it’s easier to discuss features and design the solutions of a product in plain language – and revise those ideas – than it is to do it in code.
This is the main reason why functional specifications documents exist in the first place. Plain language and diagramming makes everything clearer from the start. Developers who start working without having this document to hand often find they have problems later on with their code.
In short, the functional specification documentation doesn’t have too much technical language and jargon, but is more of a description of the various behaviors and solutions to a problem that needs to be solved for the user.
For the actual document itself, using a functional specification document template is a no-brainer. In fact, we’ve even included a few functional specification document examples below that you can download and fill in immediately.
These templates already come with a table of contents and many come with all of the sections and headers you will need. From there, all you need to do is edit each field to include the relevant information from your own project. Most of them can even be copied and pasted into your favorite word processing tool.
Templates bring big benefits for drafting functional specifications, making sure that documents across your organization look consistent and clear. This helps everyone understand the information better. Plus, they save time because you don’t have to start from scratch every time you need a new document. Teams can focus more on the actual content and worry less about how it’s formatted.
They are also flexible and can be adjusted to meet the functional requirements of your project or the standards of your organization. This adaptability makes them suitable for a variety of projects.
When picking a template, think about what your project needs and what your team prefers. It’s a good idea to look at several functional specification document examples to find the best one for your project’s size and complexity. Many platforms let you customize templates, so you can adjust them to perfectly meet your needs. Using them smartly can make the whole process smoother, reduce mistakes, and make sure nothing important is missed.
As we mentioned above, you’ll need to have some use cases ready to add in to your functional specification document. These explain the rationale for each feature and provide some context as to how the feature should work. It doesn’t have to be a big long story, just something that highlights the problem the feature will solve.
Imagine the following use case for a car rental app:
“User goes to a parking lot only to discover the car they reserved isn’t there. They check the reservation on our app which tells them the car still hasn’t been returned by the previous user and offers them another vehicle in the parking lot at a reduced price. The user can then choose to accept that vehicle or reject it. “
User flows illustrate how use cases and user scenarios are realized within your app. For this section, include diagrams of the different screens from your mockup or prototype to demonstrate the navigation paths a user might take. These visual guides are essential for ensuring that everyone involved understands how the app functions from a user’s perspective.
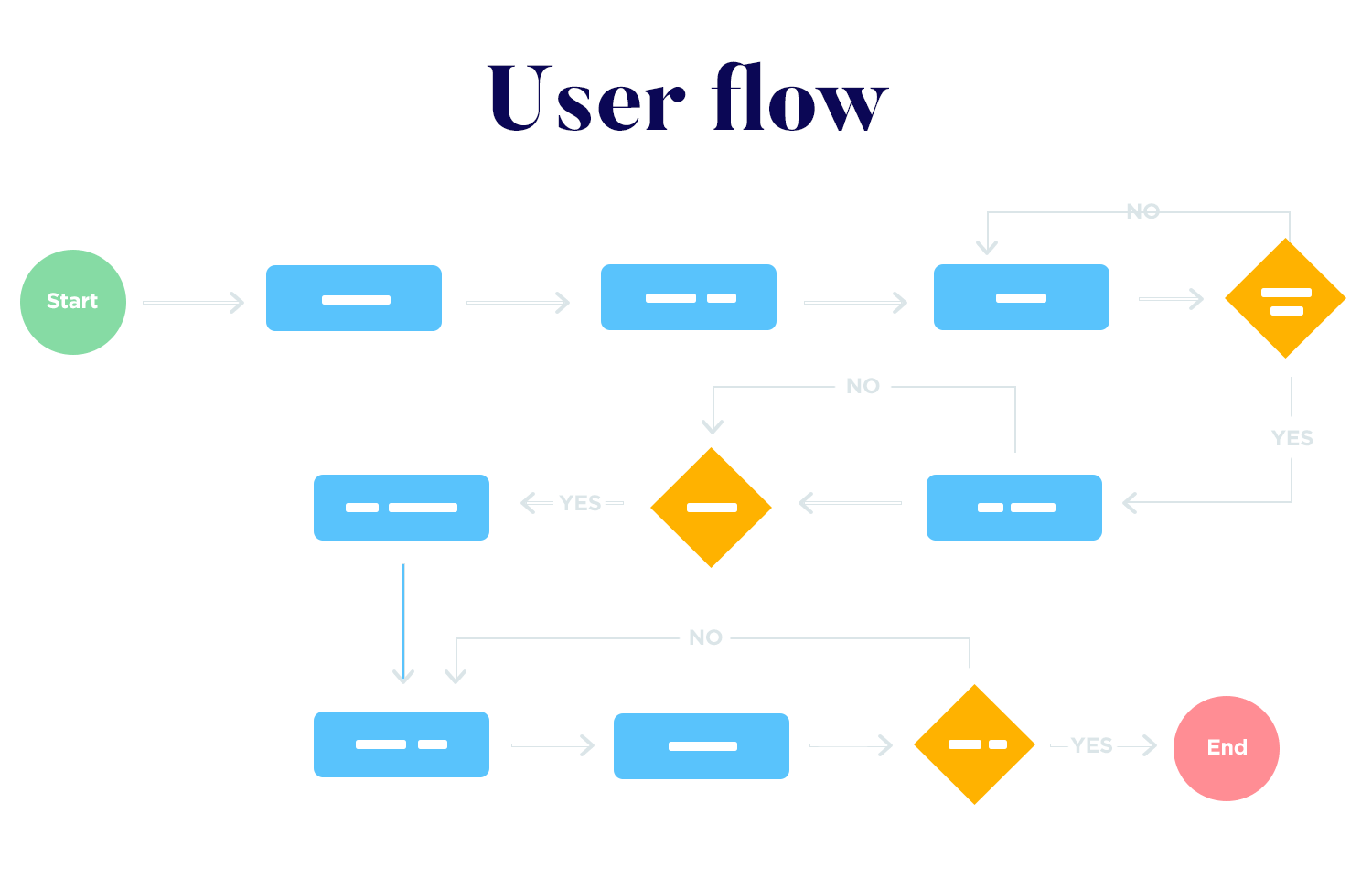
Make sure to incorporate both alternate and exception flows into these diagrams. Alternate flows can show various routes users might take, such as reaching a “car unavailable” screen either by tapping on a notification or by navigating through the app to the booking section. Exception flows should capture potential missteps, like a user accidentally entering the “reserve new vehicle” section when they meant to do something else.
The post condition will indicate the state of the app’s system after running a use case. In the case of the car rental app we mentioned above, the product’s post condition will depend on whether the user selects the new vehicle or not.
If the user takes the offered vehicle, the app starts the rental timer. This means their rental has begun, and the app might show them their rental details like return time or directions to the car.
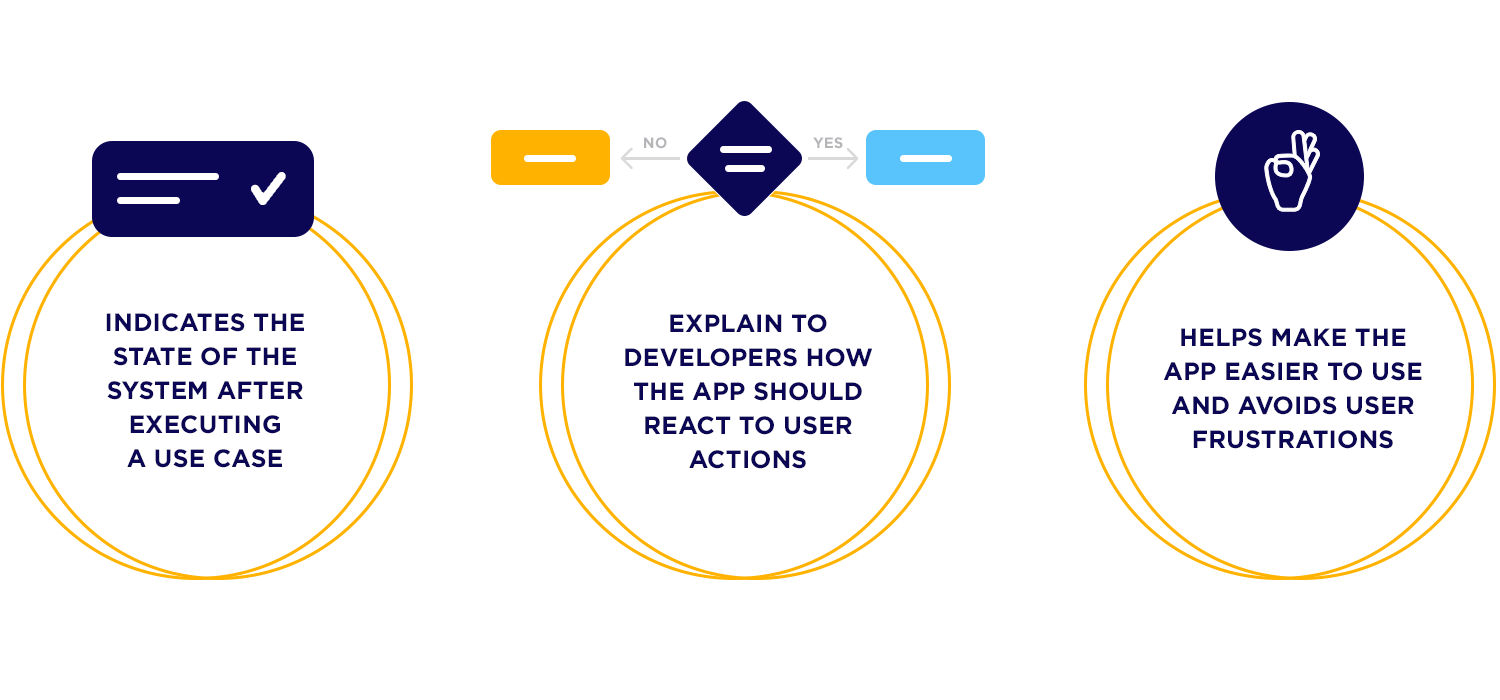
If the user doesn’t want the vehicle, the app sends them back to the booking screen. Here, they can look for another car or change their booking. This makes sure the user has options without starting all over.
Specifying these post conditions in the app’s documentation helps developers understand how the app should react to user choices. This makes the app easier to use and helps fix any issues by setting clear expectations for what should happen in each situation.
In your functional specifications document, it’s important to include links to your wireframe or prototype, as well as your shared library of assets. This should cover everything that will aid the developers in building the application, such as CSS stylesheets, and details about element spacing, padding, and color codes.
Including these links makes it easier for developers to access the visual and design elements they need without searching for them. This is especially crucial when multiple team members are working on different parts of the project, as it ensures consistency in the visual design and user interface across the entire application.
You may include a timeline or roadmap that establishes when user testing occurs, for example, after each feature design. Additionally, you may specify at what point you will have reached the MVP stage of your product that you will use with early adopters.
Lastly, once the developer has coded all of the feature specifications, then you have reached the end product. However, most of the time there will be some scope for further future iterations of the product in the form of features, new versions and updates.
In this case, the cycle is merely repeated, for which you will start with a brand new requirements statement and flesh out a new feature specification document.
Here are some great examples of functional specification documentation that you can also use as templates to start writing up your own. Quick and easy and no having to start everything from scratch!
This functional specification document template from Stanford University is a 10-page document template that contains a complete table of contents with 10 items and an appendix.
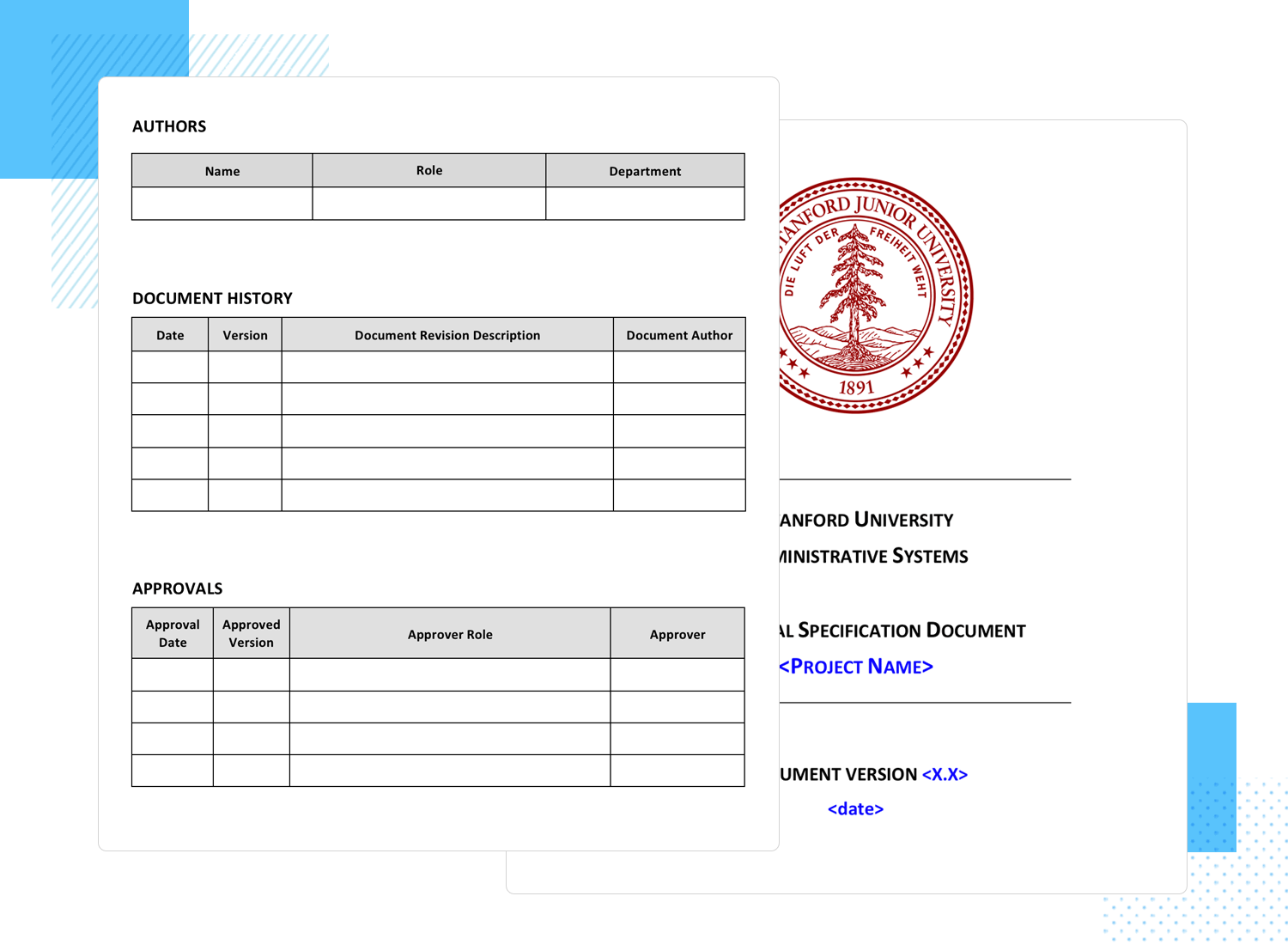
It ticks all the boxes of a complete functional specification document in that it contains risks and assumptions, project scope, business need, functional specifications and actors (users in use cases). There’s even a suggested part of the document to leave a link to your mockup or prototype, as well as a table for the development team to fill in ticketing issues.
If it’s a website you’re creating, be it an e-commerce or a blog, and you’re looking for a basic template – this functional specification document template from Smartsheet is the answer.
This short template comes with questions that ask you to write in the details about your planned website without any technical knowledge required. It includes sections such as the purpose and business goals of the website, the target user personas and the organization of the website.
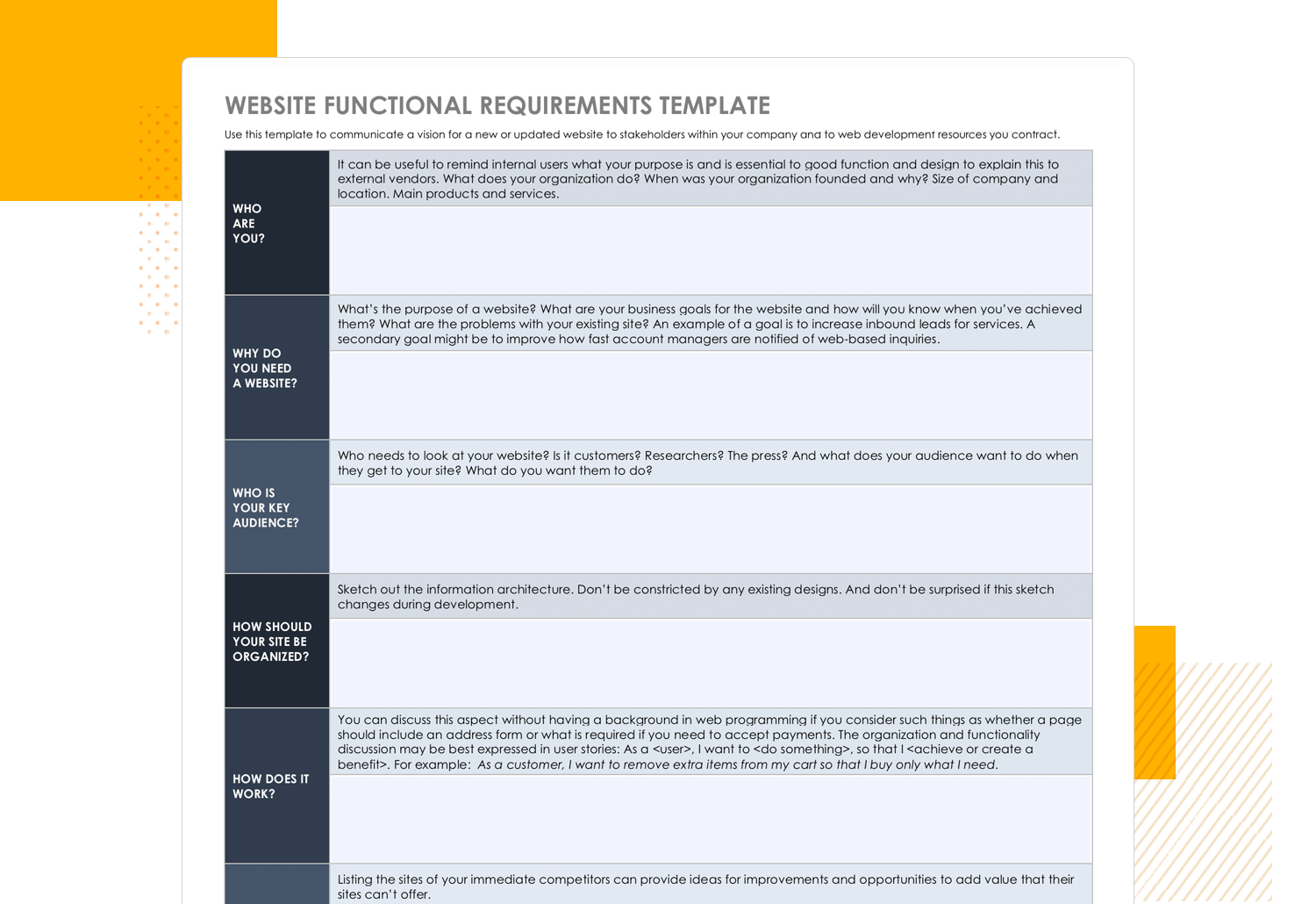
It also has a section prompting you to sketch out the information architecture, along with how the features of the website should behave, making it a good option for simplicity and clarity.
If you’re looking for an exhaustive, well-structured template that has everything logically laid out and easy to find, then this is the functional specification document from the Project Management Institute you want to be copying. It’s based on a PMP software system to be used by pharmacists for prescription reporting.
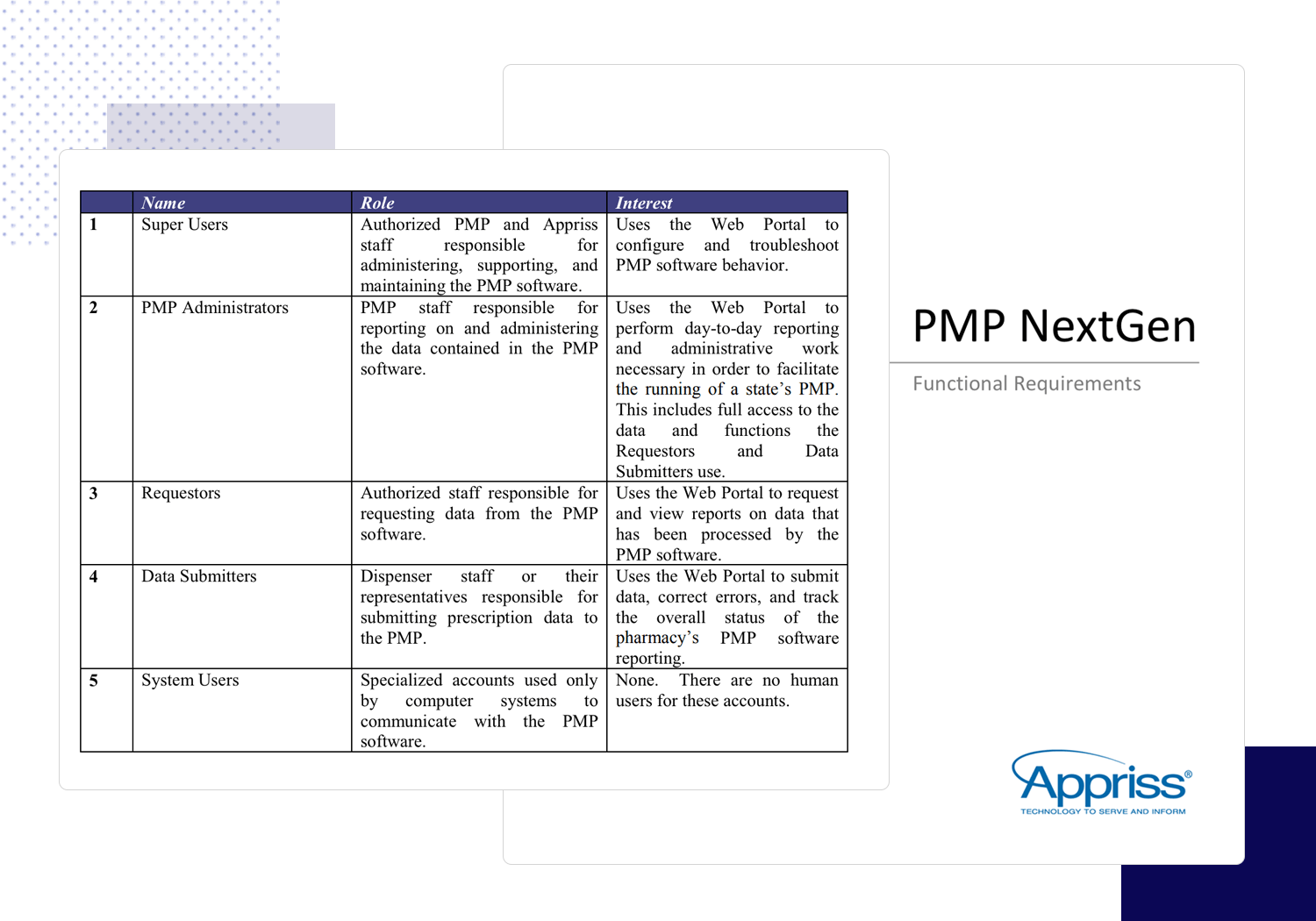
It serves as a brilliant example of how to integrate use cases, screen mockups and user flows in one document. It’s clear hierarchical numerical layout means that anyone who reads the document can easily navigate to any element within the document using the index.
Klariti is a website that offers various templates for sale for the many different document deliverables needed if you work in software, web and app development. They offer documents for software testing, development, business process design and case studies.
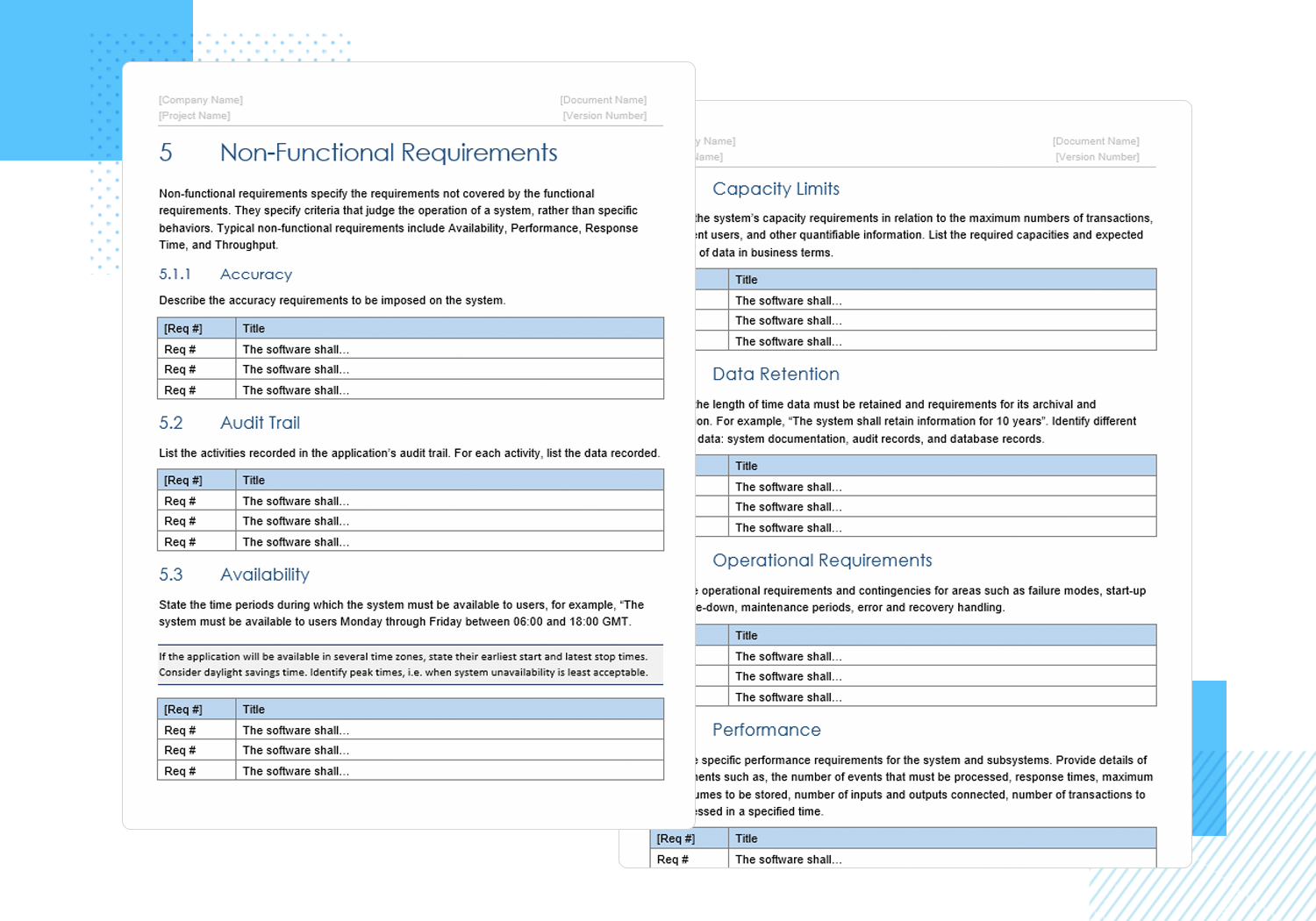
Klariti’s 27-page functional specification document template comes in MS Word format. It helps you to define how a piece of software will function and how it will behave when the user provides it with certain inputs, or when certain conditions arise out of a specific situation.
The Klariti template lets you enter in specifications for functions involving data manipulation, data processing, calculations, conditions and more. It’s available on their site for $9.99.
This GitHub-based template is straightforward and flexible. It’s designed to be easily adaptable, providing a clear format for listing requirements, use cases, and workflows. It’s a great fit for teams that need a quick, organized way to document their project needs while keeping things agile.

For teams that succeed in dynamic environments, these functional specification document templates from Notion offer a collaborative advantage. The platform is well-known for its strong teamwork features and flexible formatting, making it ideal for projects with frequent adjustments and ongoing updates.
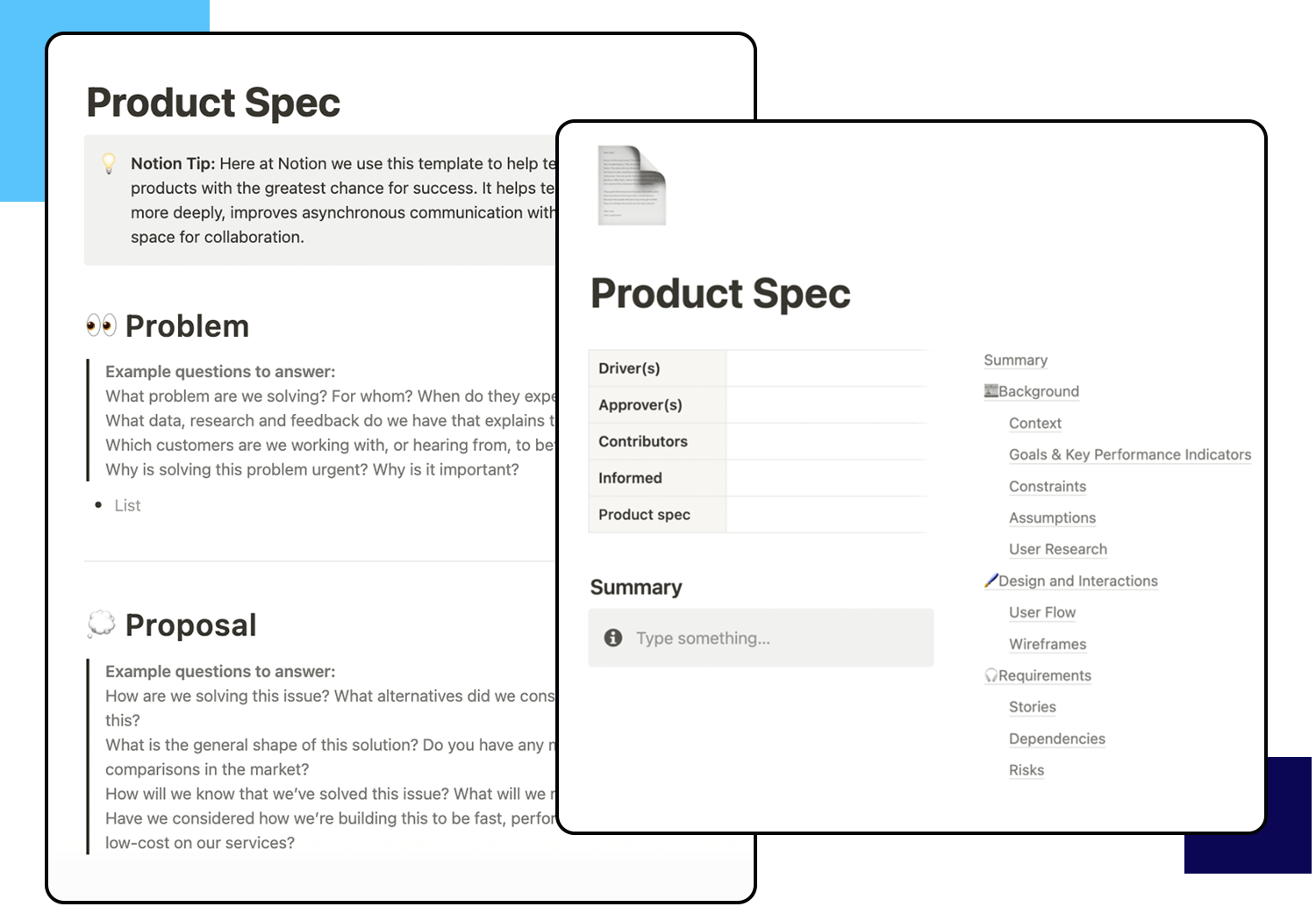
These templates streamline the organization of feature details, user narratives, acceptance requirements, and release plans within a highly interactive workspace. Team members can easily comment, assign tasks, and track progress directly in the document, fostering clear communication and transparency.
This solution is particularly well-suited for agile projects, integrating smoothly with workflows that emphasize continuous feedback and active team involvement.
If you’re looking for a flexible and easy-to-use template, ClickUp offers a versatile and easy-to-use functional specifications template that’s great for teams looking for flexibility. It helps you organize key project details, from requirements and use cases to workflows and timelines, all in one place.
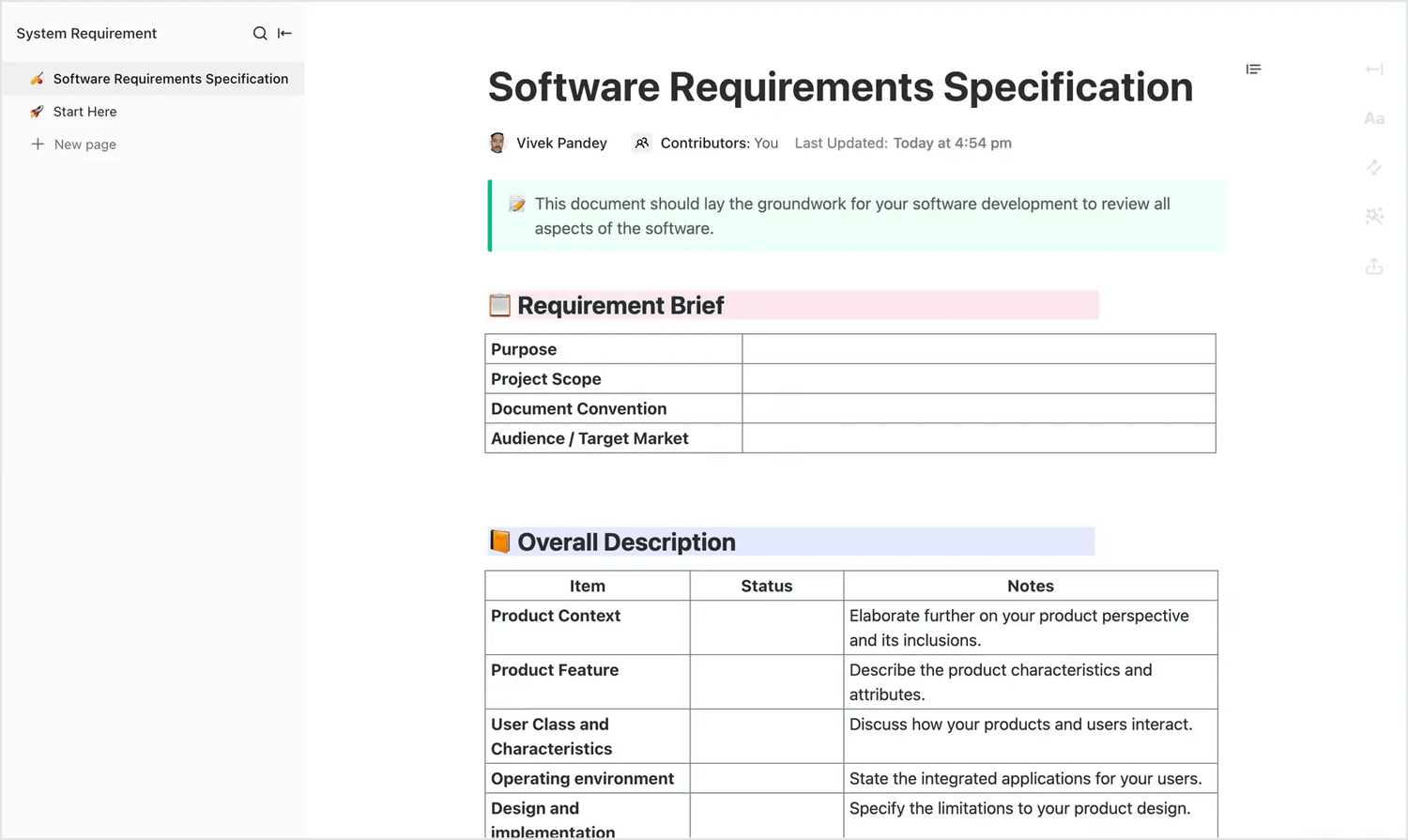
What’s great about this template is that it’s designed for collaboration – team members can leave comments, track progress, and make adjustments in real time. Whether you’re building software, managing a website, or tackling a complex project, ClickUp’s template makes it simple to keep everyone on the same page.
For a more academic approach, Studocu offers a functional specification template that’s often used in software engineering courses. This template lays out the structure in a clear, organized way, helping you capture everything from system requirements to design specifications. It’s a great resource if you’re looking for a more detailed and structured format, especially for educational or research-based projects.

What makes this template useful is its focus on covering all the bases, making sure nothing gets overlooked as you plan and document your project.
If you’re working on SAP systems or enterprise-level projects, this sample from Scribd is a great resource. It’s specifically designed for SAP SD (sales and distribution) projects, offering a detailed look at how to document functional specifications for large-scale software solutions.
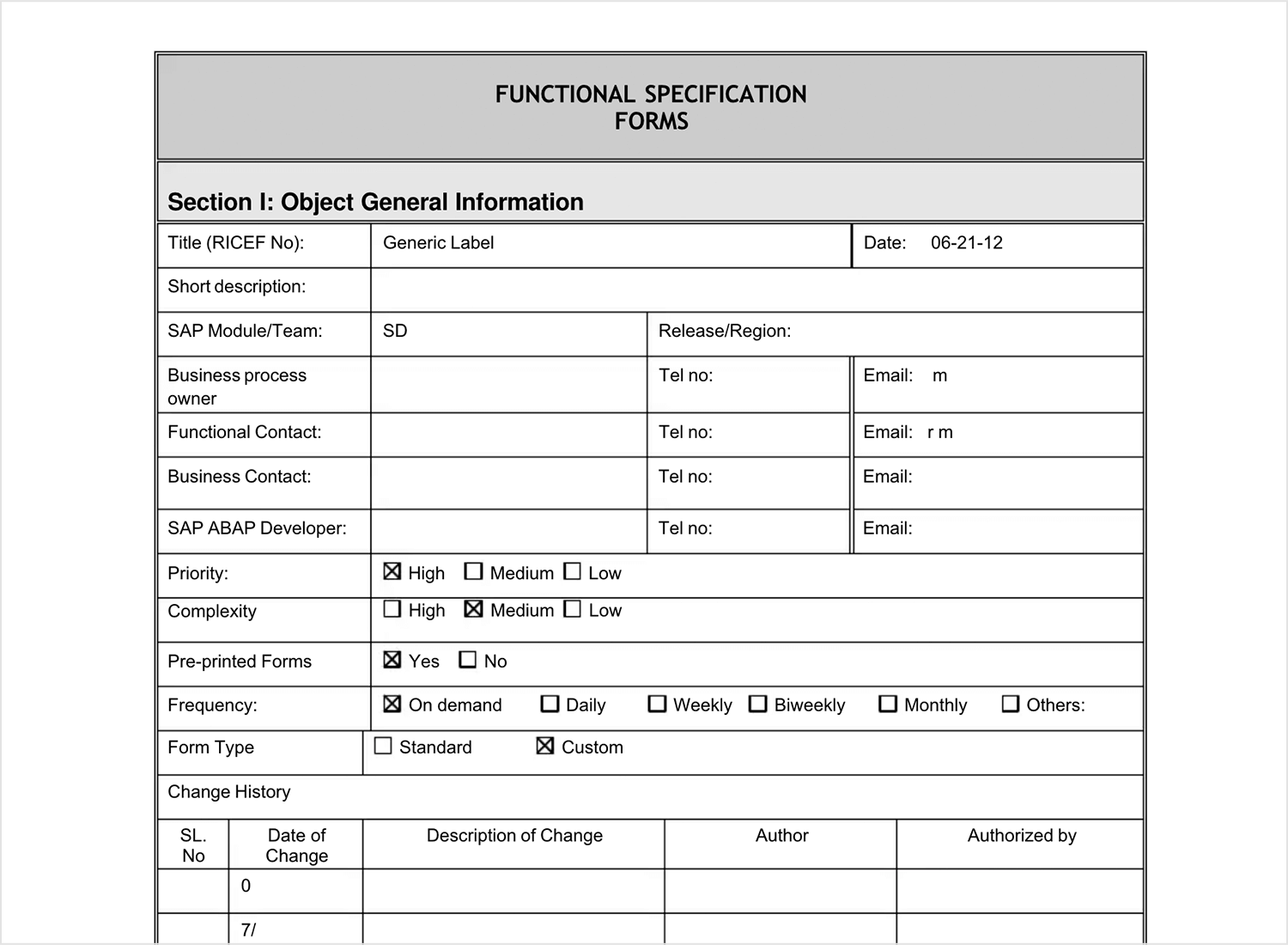
This template walks you through everything, from outlining business processes to defining system requirements and configurations. It’s especially helpful if you’re navigating the complex world of SAP, providing a structured way to capture all necessary details without missing anything important.
Last on our list is TechTransform’s template, perfect for anyone needing a no-fuss, professional approach. This template covers all the core areas, from functional requirements to business logic and system behavior. It’s laid out in a way that makes it simple to follow, making sure everything is clearly documented from the start.
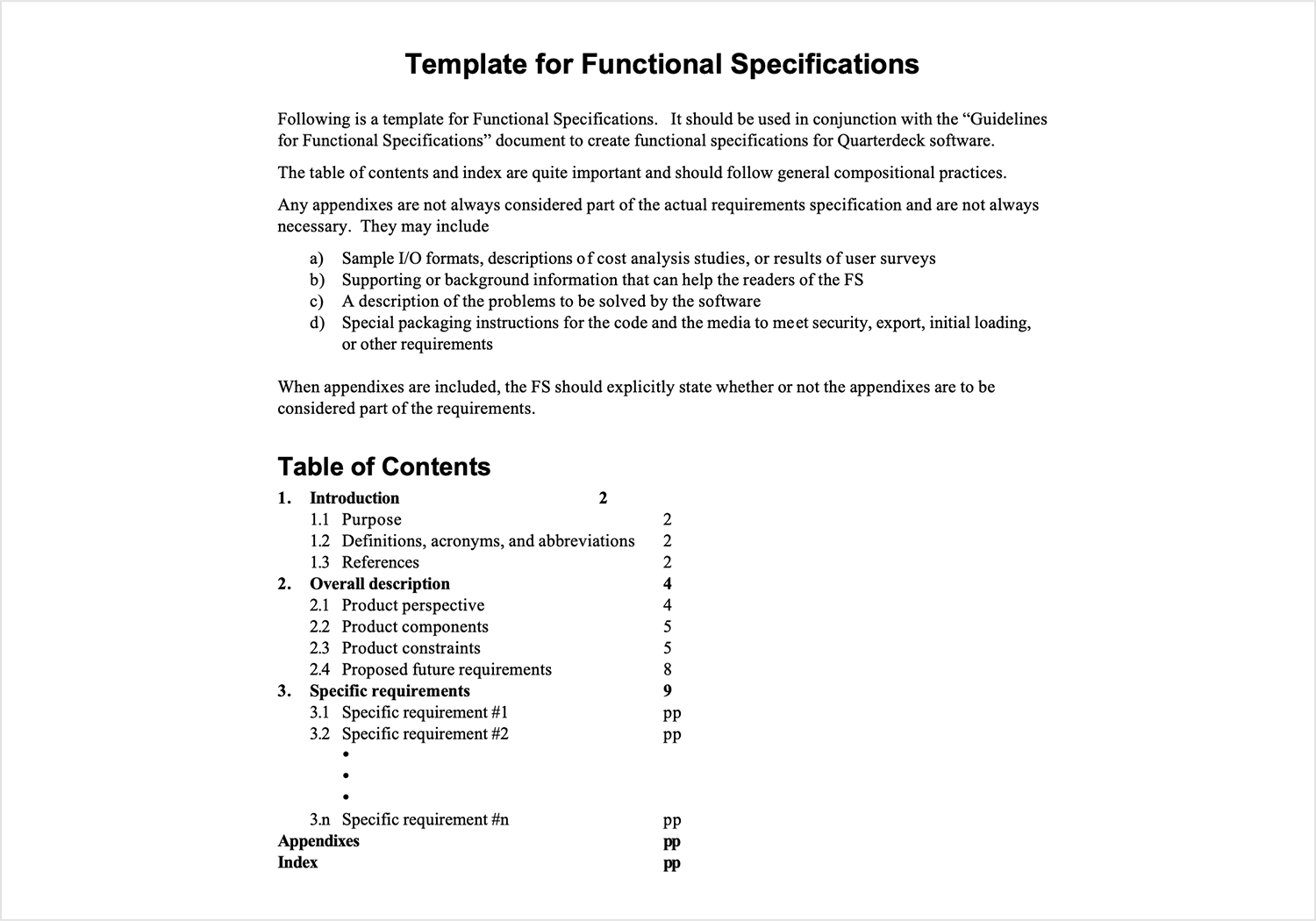
If your team values clarity and staying on track, this template will fit right in. It’s a solid option to wrap up our list, providing a reliable foundation for your project’s specifications.
Did you know that you can actually test out your functional specifications and validate them when you reach the prototype stage? Wireframes and prototypes often rely on visual aids to map out how a system will function. These visual representations, often basic sketches or low-fidelity models, help visualize complex concepts and ensure the design aligns with user needs before investing in extensive development work.
Using Justinmind, you can quickly and easily test out your product’s functionality on your users before you get to the coding stage by using it in conjunction with integrated tools such as UserTesting and Hotjar. That’s just what one of our clients, Judit Casacuberta Bagó from Scytl, does!
Judit uses the Justinmind Events system to add complex interactions, allowing her to recreate a workflow based on functional requirements. This in turn allows her and the team to evaluate how each touchpoint impacts the product as a whole. This practical application highlights how functional specification document templates can be utilized effectively.
Her team then exports their prototypes to HTML. Subsequently, Judit typically walks her client through the main workflows, target users, and the feature functionalities. Prototyping tools are not limited to Justinmind; others like Sketch, Adobe XD, and Figma also offer powerful features for creating dynamic wireframes and prototypes. Each tool has its strengths, and selecting the right one can depend on the specific functional specifications of your project.
When it comes to requirements generation and functional specification documentation, Justinmind serves as an effective tool. The ability to generate documentation automatically before source code is written is both useful and quick. Quick because you don’t need to spend time creating lengthy documents and useful because your developers will be able to understand exactly what you want.
In the Justinmind interface, there’s a tab on the top right called Requirements. Here in the requirements module, you’ll find a comprehensive view of all the Requirements, including version histories, related components, and comments. For deeper insights using tools like these, consider exploring the Justinmind requirements management blog post.
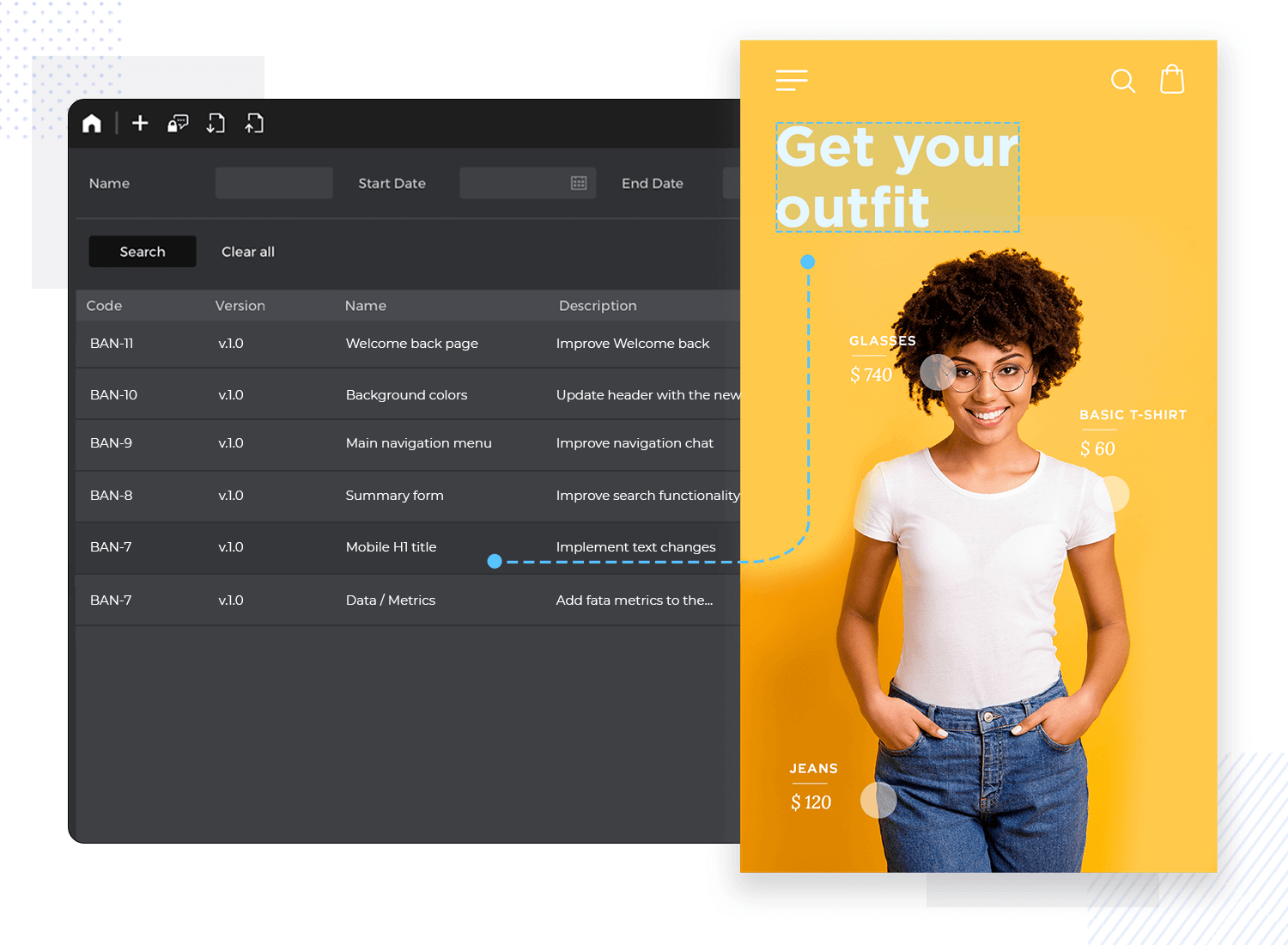
Requirements module in Justinmind
The widgets you place on your canvas can be turned into requirements, simply by right clicking on them. These features enable teams to work in a truly collaborative manner, which is handy if you ever want to reach a consensus.
It’s also possible to categorize requirements using colors and labels which results in a stronger grip on version control (because there’s nothing worse than being lost in twelve different versions of the same thing).
To give your entire team full visibility and enhance collaboration, Justinmind lets you effortlessly integrate with JIRA, too. A click of the button (or more precisely: File > Export to Document) and you’ll have your documentation — visuals and all!
Imagine functional specification documents as the roadmap for your software project. They help to prevent costly misinterpretations, inefficient use of time and resources, and a final product that falls short. These documents define the features, objectives, and overall direction of the project, helping everyone on the team share the same understanding.
Dedicating time early on to create a detailed functional specification streamlines the development process. It promotes clear understanding among everyone involved, from developers to stakeholders. The payoff? Reduced delays, smoother workflow, and overall greater efficiency.
Teams that prioritize these documents often experience smoother projects and happier teams. Investing in a strong foundation helps ensure the final product delivers on its promises.
PROTOTYPE · COMMUNICATE · VALIDATE
ALL-IN-ONE PROTOTYPING TOOL FOR WEB AND MOBILE APPS
Related Content
 Learn how to design better e-learning platforms with user-centered UX principles, real examples, and high-fidelity prototyping tips to boost engagement and learning outcomes.13 min Read
Learn how to design better e-learning platforms with user-centered UX principles, real examples, and high-fidelity prototyping tips to boost engagement and learning outcomes.13 min Read Infinite scroll keeps users engaged, but it’s not always the best choice. This guide breaks down when to use it, when to avoid it, and how to design it right.14 min Read
Infinite scroll keeps users engaged, but it’s not always the best choice. This guide breaks down when to use it, when to avoid it, and how to design it right.14 min Read What is data visualization, and why is it useful? This post explains how turning complex data into simple visuals like charts and graphs helps you understand and use information better.28 min Read
What is data visualization, and why is it useful? This post explains how turning complex data into simple visuals like charts and graphs helps you understand and use information better.28 min Read